Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is an increasingly common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many are unaware of its signs and symptoms, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Dr. Pawan Rawal, a renowned gastroenterologist in India, offers insights into this condition and emphasizes the importance of early detection and specialized care at advanced liver clinics.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. There are two main types: Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD), caused by excessive alcohol consumption, and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), which occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol. NAFLD is more common and is often associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
Signs and Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
One of the challenges of diagnosing fatty liver disease is that it often presents no symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, as the disease progresses, several signs and symptoms may emerge.
1. Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic fatigue and general weakness are common symptoms of fatty liver disease. Patients often feel unusually tired even after adequate rest, which can affect daily activities and overall quality of life.
2. Abdominal Discomfort
Many individuals with fatty liver disease report a dull or aching pain in the upper right abdomen, where the liver is located. This discomfort is due to the liver enlarging and pressing against surrounding organs and tissues.
3. Weight Loss and Loss of Appetite
Unexpected weight loss and a decreased appetite can be indicators of fatty liver disease. These symptoms often result from the body’s impaired ability to metabolize nutrients effectively due to liver dysfunction.
4. Jaundice
Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, occurs when the liver is unable to process bilirubin effectively. This condition indicates significant liver damage and requires immediate medical attention.
5. Swelling in the Abdomen and Legs
Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites) and swelling in the legs (edema) are signs of advanced liver disease. These symptoms suggest that the liver is not functioning properly and is struggling to manage fluid balance in the body.
6. Mental Confusion
In severe cases, fatty liver disease can lead to hepatic encephalopathy, a condition characterized by confusion, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems. This occurs when the liver cannot remove toxins from the blood effectively, allowing them to reach the brain.
Risk Factors for Fatty Liver Disease
Understanding the risk factors for fatty liver disease can help in its prevention and early detection. Key risk factors include:
- Obesity: Excess body fat is a primary risk factor for NAFLD.
- Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance are closely linked to fatty liver disease.
- High Cholesterol and Triglycerides: Elevated levels of fats in the blood can contribute to liver fat accumulation.
- Metabolic Syndrome: This cluster of conditions, including hypertension, high blood sugar, and abdominal obesity, increases the risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking is the leading cause of AFLD, but even moderate alcohol intake can exacerbate liver problems in individuals with NAFLD.
Diagnosis and Treatment of fatty Liver
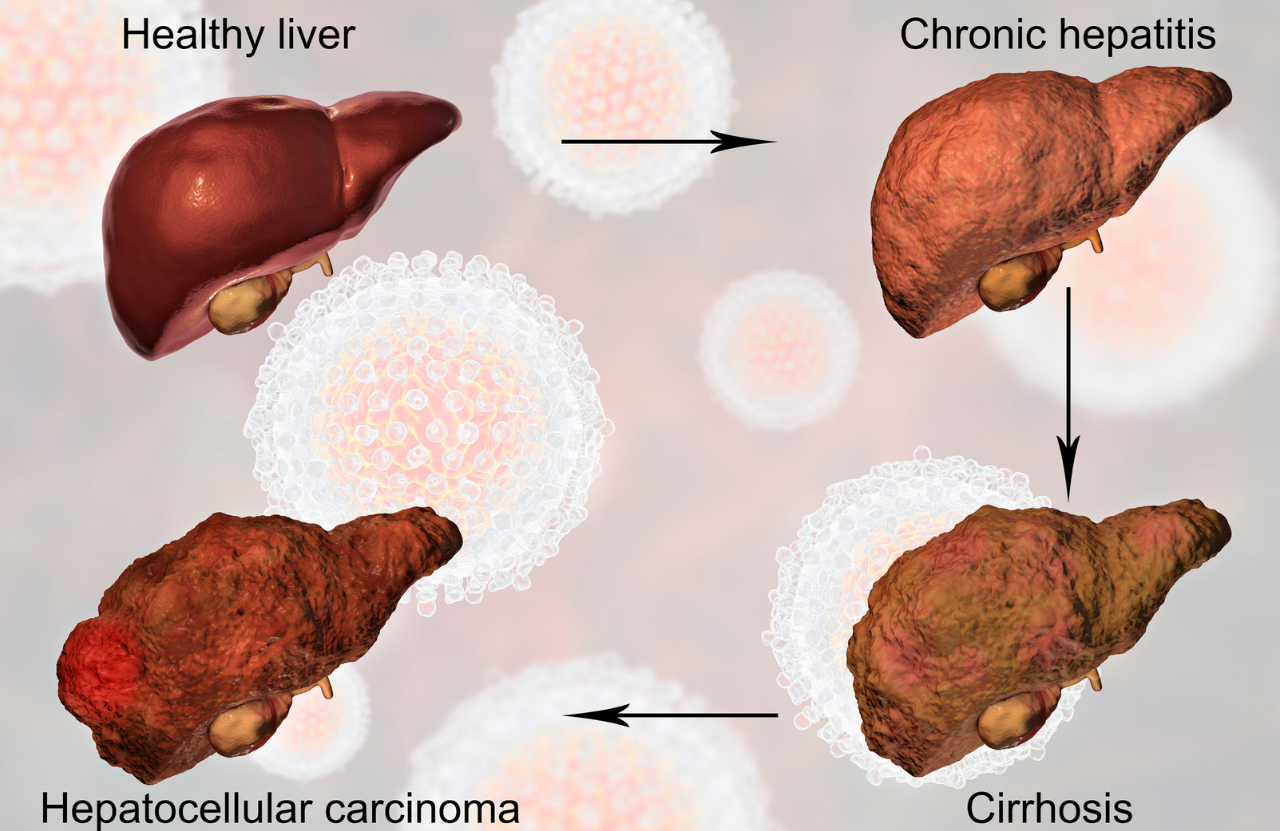
Early diagnosis of fatty liver disease is crucial to prevent progression to more severe conditions such as cirrhosis or liver cancer. At an advanced liver clinic like the one operated by Dr. Pawan Rawal, comprehensive diagnostic tests are employed to assess liver health. These tests may include blood tests, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI, and sometimes liver biopsy.
Lifestyle Modifications
For many patients, lifestyle changes can significantly improve liver health. Key recommendations include:
- Weight Loss: Gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce liver fat.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while low in saturated fats, refined sugars, and alcohol is beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps manage weight and improve insulin sensitivity, reducing liver fat.
- Avoiding Alcohol: Abstaining from alcohol is essential for those with AFLD and beneficial for those with NAFLD.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, or to reduce liver inflammation.
The Role of Advanced Liver Clinics
Advanced liver clinics provide specialized care for patients with liver diseases. These clinics, such as the one led by Dr. Pawan Rawal, a leading gastroenterologist in India, offer a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. This includes access to hepatologists, dietitians, and other specialists who work together to create personalized treatment plans.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a silent but serious condition that requires attention and care. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early can lead to better outcomes and prevent severe liver damage. For those at risk or experiencing symptoms, seeking evaluation and treatment at an advanced liver clinic is crucial. Dr. Pawan Rawal and his team provide comprehensive care and support for patients, guiding them toward improved liver health and overall well-being.
By addressing the condition with the expertise of a renowned gastroenterologist in India and leveraging the resources of an advanced liver clinic, patients can navigate their journey to recovery with confidence and hope.